Get Healthy!
Staying informed is also a great way to stay healthy. Keep up-to-date with all the latest health news here.
19 Feb
Spirituality Linked to Lower Risk of Alcohol and Drug Misuse
A new study links spiritual or religious involvement to a significantly lower risk of harmful alcohol or drug use.
18 Feb
Sugary Drinks Tied to Adolescent Anxiety in New Study
Teens who regularly drink large amounts of sugar-sweetened beverages — including soda, energy drinks, sweetened teas and coffee drinks — are more likely to report symptoms of anxiety.
17 Feb
1 in 4 Teens Sending Sexts — Many Face Blackmail, New Study Warns
A new survey of nearly 3,500 teens finds a surge in sexting since 2019 and an increase in sextortion or blackmail.
Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter February 19, 2026
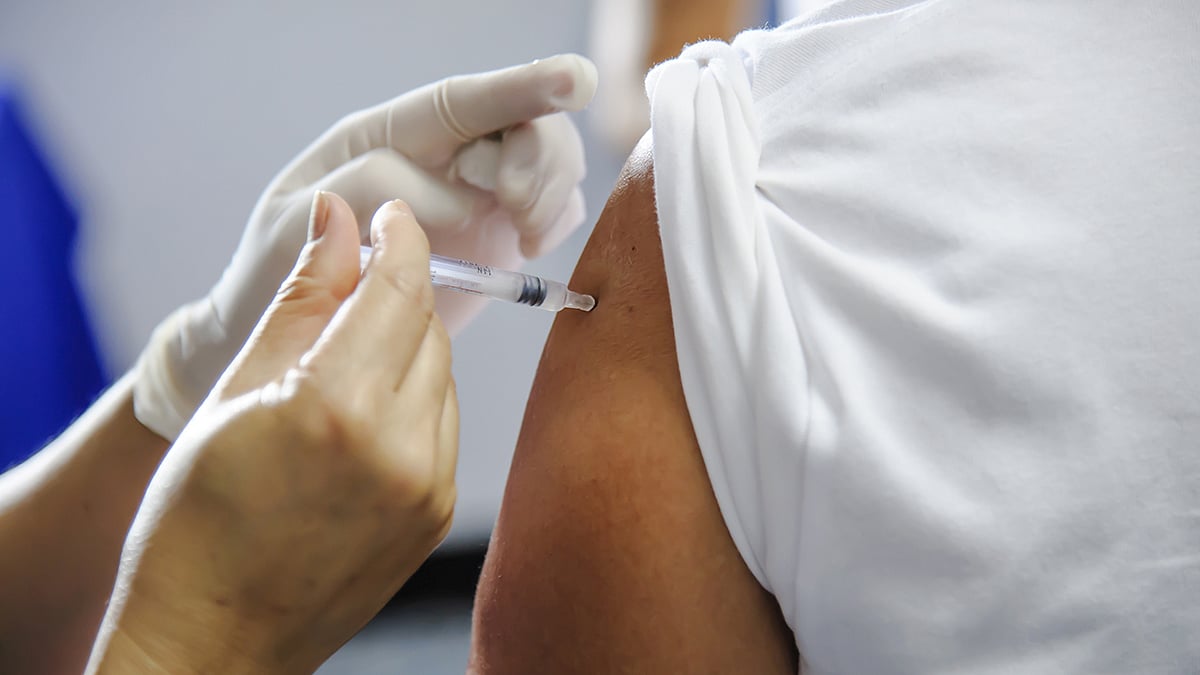
Moderna’s mRNA Flu Vaccine Back Under FDA Review
In a sudden reversal, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has agreed to review Moderna’s experimental mRNA influenza vaccine.
The move comes just one week after the agency refused to evaluate the company’s application, a decision that sent shockwaves through the biotech industry.
The initial rejection center... Full Page
Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter February 19, 2026
BJ’s Wholesale Club Issues Salmon Recall Across Seven East Coast States
If you recently bought frozen salmon at BJ’s Wholesale Club, check the packaging before your next meal.
Wellesley Farms Farm-Raised Atlantic Salmon is being pulled from shelves across seven states after federal testing found it contained dangerous bacteria.
The recall involves 2-pound bags of the frozen fish. The af... Full Page
Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter February 19, 2026
Sweetened Drinks Linked to Higher Anxiety in Teens
While parents have long worried that too much sugar leads to cavities and weight gain, new research suggests that sugar rush might be followed by a worry crash.
A study from Bournemouth University in the U.K. has identified a troubling link between high-sugar drinks and increased anxiety symptoms in young people.
Researchers re... Full Page
Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter February 19, 2026
Drug-Resistant Salmonella Linked to Moringa Supplement
It's often touted as the "miracle tree" for its dense nutrient profile, but a popular moringa supplement is at the center of a superbug outbreak.
Federal health officials announced Feb. 13 that a multistate outbreak of highly drug-resistant Salmonella has been traced back to moringa powder capsules.
The investigation, conduc... Full Page
Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter February 19, 2026
It's Never Too Late For Cancer Patients To Become Active, Study Finds
It’s never too late for cancer survivors to become active, a new study reports.
Cancer survivors who engaged in even small amounts of exercise reduced their risk of cancer-related death, researchers reported Feb. 17 in JAMA Network Open.
That risk dropped even more among patients who achieved higher levels of physical ... Full Page
Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter February 19, 2026
Ultra-Marathon Running Depletes Athletes' Red Blood Cells, Study Finds
Ultra-marathon runners must be incredibly fit to endure races that can extend more than 100 miles, but their bodies pay a price for their athleticism, a new study says.
Extreme endurance runners experience a breakdown of their normal red blood cells during a race, putting them at increased risk of anemia, researchers reported Feb. 18 in th... Full Page
Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter February 19, 2026
Rates Of Hearing Loss, Tinnitus More Than Doubled Among Musicians
Musicians suffer hearing loss in pursuit of their passion more than twice as often as average folks, a new evidence review says.
More than 2 in 5 musicians suffer from tinnitus and a quarter are affected by hearing loss, researchers recently reported in the journal Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.
“Many musi... Full Page
Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter February 19, 2026
Ancient Chinese Practice Lowers Blood Pressure As Well As Medications, Walking Program, Clinical Trial Shows
An ancient Chinese mind-body practice can lower a person’s blood pressure as well as medication or a program of brisk walking, a new study says.
Baduanjin is a widely practiced eight-movement sequence that combines slow, structured movement, deep breathing and meditation.
The practice lowered people’s blood pressure by ab... Full Page
Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter February 19, 2026
U.S. Parents Report Gaps in Accessing Mental Health Care for Their Child
Despite a growing mental health crisis among America’s youth, the system is still failing a massive number of children, a large study suggests.
Nearly one-quarter of children who need mental health treatment are not receiving it, according to the analysis led by researchers at the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute in Boston... Full Page
Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter February 19, 2026
Robotic Pets Help Dementia Patients Recover and Return Home
For a person living with dementia, a hospital stay can be a terrifying whirlwind of strange faces, loud noises and confusing tests.
This disorientation often leads to a condition called delirium, which can slow down recovery and lead to more time spent in medical facilities.
However, a clinical trial sponsored by Sarasota Memor... Full Page
I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter February 18, 2026
Bananas From a Decade-Old Mining Spill Area in Brazil May Be Unsafe, Research Says
More than a decade after a major mining disaster in Brazil, scientists are still uncovering its health effects, including potential risks from food grown in nearby soil.
A new study suggests that bananas grown near the Doce River estuary may pose health risks for children under 6, due to lingering contamination from iron mining waste relea... Full Page
I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter February 18, 2026
Mandy Moore Shares Why RSV Protection Became a Priority for Her Family
When actress and singer/songwriter Mandy Moore talks about RSV, it’s not just as a celebrity, it’s as a mom who’s lived through it.
In 2023, both of Moore’s sons came down with respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV, at the same time. The experience, she says, was overwhelming.
“I just will not forget how h... Full Page
I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter February 18, 2026
NIH Institute Told To Drop ‘Biodefense’ and 'Pandemic Preparedness' Language From Website
As new infectious threats emerge worldwide, a key U.S. health agency is quietly stepping away from language tied to pandemic planning, a change some experts warn could leave Americans less protected when the next crisis hits.
Staff at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) have been told to remove references to &... Full Page
I. Edwards HealthDay Reporter February 18, 2026
Peanut Butter Sold in 40 States Recalled Over Possible Plastic Contamination
If you have peanut butter at home, federal health officials say it’s worth taking a closer look.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has announced a recall of more than 20,000 peanut butter products after pieces of plastic were found during the manufacturing process.
The peanut butter was made by Ventura Foods and sold ... Full Page
Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter February 18, 2026
Want To Preserve Brain Health? Engage In A Lifetime Pursuit Of Knowledge, Study Says
“Anyone who stops learning is old, whether at 20 or 80,” American entrepreneur Henry Ford once said. “Anyone who keeps learning stays young.”
There’s something to that, a new study says.
People who engage in a lifetime pursuit of learning have a lower risk of Alzheimer’s disease, as well as slower ... Full Page
Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter February 18, 2026
'Smart Clothing' The Next Frontier In Fitness Tracking, Study Says
Health-conscious folks are used to strapping a Fitbit to their wrist or a step counter to their belt before they start walking or jogging.
But new research is opening the door to “smart clothing” that would count a person’s steps or track their movement without requiring any extra gadgets, a new study says.
Breakthr... Full Page
Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter February 18, 2026
Pain Drives Postpartum Depression, Review Finds
Pain during pregnancy and after delivery can significantly increase a woman’s risk of postpartum depression, a new evidence review has concluded.
Further, there are specific pain-related risk factors that influence the odds of postpartum depression among women in racial and ethnic minorities, researchers reported in the journal C... Full Page
Dennis Thompson HealthDay Reporter February 18, 2026
Shame, Embarrassment Regarding Walking Problems Can Isolate MS Patients
A mom with multiple sclerosis (MS) struggled to keep her balance, frustrated by her frequent missteps and stumbles.
But what really hurt was her 6-year-old daughter’s reaction to her plight.
“My daughter told me to stop walking with them basically because it’s embarrassing when I fall,” the mother recounted in... Full Page
Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter February 18, 2026
Heavy Wildfire Smoke During Pregnancy May Be Linked to Increased Autism Risk
As wildfires become more frequent and severe across the Western United States, new research suggests the thick blankets of smoke they produce may have long-lasting effects on fetal development.
A study of millions of California births has found a link between exposure to intense wildfire smoke during pregnancy and an increased likelihood o... Full Page
Deanna Neff HealthDay Reporter February 18, 2026
School Stress at Age 15 May Leave Long-Term Mental Health Scars
The intense pressure to succeed academically at age 15 may cast a long shadow, increasing the risk of depression and self-harm well into a person's 20s, a new study says.
While many parents and teachers view high expectations as a necessary push toward success, the research suggests that for many, the "push" becomes a "shove" that damages ... Full Page










.jpg?w=1920&h=1080&mode=crop&crop=focalpoint)









